China used anti-dumping rules against us because what goes around comes around
Australia has acted with dismay to China’s decision to impose punitive mostly “anti-dumping” tariffs of 80.5% on imports of Australian barley.
The culmination of an 18-month investigation, China’s move threatens to wipe out Australian barley exports to China, worth A$600 million in 2019, unless China withdraws the measure either unilaterally or following a successful challenge at the World Trade Organisation (WTO).
However poorly justified, there are precedents for what China has done, many of them from Australia.
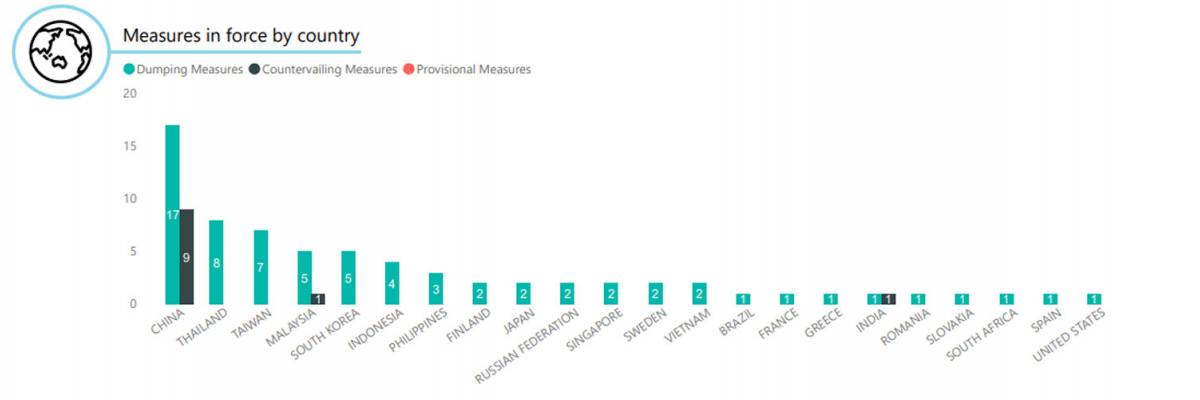
Australian anti-dumping and countervailing measures by country, March 2020
Australia was among the first wave of countries to adopt anti-dumping legislation alongside Canada, New Zealand, the United States and Britain in the early years of the 20th Century.
It remains a prolific user of the system compared to other countries, with an outsized number of measures imposed against imports from one country, China, and imports of one product, steel.
What are anti-dumping measures?
One way to think about anti-dumping measures is the international equivalent of domestic measures intended to combat predatory pricing.
Guidance from the Australian Competition and Consumer Commission says that while it is usually okay to sell goods at a below-cost price, “it may be illegal if it is done for the purpose of eliminating or substantially damaging a competitor”.
But in the case of international anti-dumping measures, there is no need to prove purpose.
It suffices that an investigation finds the imported goods were sold below their corresponding price in the home market and that this caused or threatened to cause harm to a domestic industry producing the same sort of goods (known as “like products”).
Chinese steel, glass, cables and A4 copy paper
Technically, Australia imposes two types of measures: “anti-dumping measures”, which are additional duties on so-called dumped imports which are held to have injured Australian industry, and “countervailing measures” which are additional duties on subsidised imports that have injured Australian industry.
They are currently in place or proposed against Chinese wind towers, glass, electric cables, chemicals, herbicides, A4 copy paper and aluminium products, as well as steel.
In theory, WTO rules only allows anti-dumping measures for limited periods (China’s measures on barley have been imposed for five years) but in practice, once in place these measures can be difficult to remove.
They shield us from cut-throat competition
In the broader context of Australia’s relationship with China, they play an important role, shielding Australian import-competing industries from the full and potentially crushing impact of free trade with China.
One aspect of their use that has been particularly galling to Chinese officials is Australia’s failure to follow through on a commitment it made during the China-Australia Free Trade Agreement negotiations to treat China as a market economy for the purpose of anti-dumping investigations.
The concession was seen as highly significant by China and would have made it harder for Australia to conclude that some goods were not being sold at fair prices.
Australia’s continued use of anti-dumping measures has come under repeated criticism from the Productivity Commission, almost entirely on the basis of economic efficiency arguments.
However, these criticisms ignore a number of important concerns, including the need to keep these measures so they can be used to hit back against other countries that use them. It would make little sense to remove them until other big users agreed to do the same.
Another important consideration, which has received greater attention during the current coronavirus crisis, is the need for – systemic resilience. If Australia becomes totally reliant on other countries for (say) steel, it’ll have less ability to get it when it is needed.
Before asking ourselves whether we are prepared to liberalise or do away with our current anti-dumping regime, we need to be able to answer the very important question of whether we are equally prepared to do away with our domestic steel, aluminium, paper and other industries.
I suspect that the answer to this question is no.
There are of course other ways to reinforce these industries or shield them from import competition, but it is more than likely that none would be as effective as the current system of anti-dumping duties. We have kept them because we still have some use for them.
By Simon Lacey, Senior Lecturer in International Trade, University of Adelaide
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
This work is licensed under Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
IIT is a global leader in researching, analysing and commenting on International Trade.
Stay informed about our up-and-coming seminars, events, publications, awards, new projects and collaborations, and other exciting news.
